In this tutorial I'll show you how to disable NMI watchdog in Linux in 4 different ways.
Few application like CoreFreq needs to disable NMI watchdog for better accuracy and performance.
The word NMI stands for Non-maskable interrupt, it's a kind of non-recoverable hardware error, that the operating system can't ignore.
In Linux, these hardware related errors could freeze up the system and you've to reboot the system manually.
That's when NMI watchdog is useful. The watchdog timer is waiting for interrupts, if there's no interrupt received for a certain amount of time, it assumes that the system is locked up and initiates a reboot or kernel panic and generates a debug log. Lets explore the methods one by one.
Contents
1. Temporarily disable NMI watchdog with sysctl command
It's very easy to disable NMI watchdog with the sysctl command line tool.
sudo sysctl kernel.nmi_watchdog=0
If the command is successfully executed, it should return like below.
kernel.nmi_watchdog = 0
You can double check by running the cat /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog command, it should return 0.
2. Disable NMI watchdog in Linux through procfs interface
The procfs is a special filesystem in Linux, used to get and manipulate various process and kernel related parameters.
It's accessible under the /proc directory on most Linux distribution.
You can use the echo command to set the nmi_watchdog value to 0 , this command needs root privilege.
sudo -i # Login to a root shell echo '0' > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog
There's other way to do the same thing,
sudo sh -c "echo '0' > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog"
3. Permanently disable through the sysctl.conf file
If you want to permanently disable NMI watchdog, just add kernel.nmi_watchdog=0 parameter to the end of the /etc/sysctl.conf file.
A single line of command to do the job.
sudo sh -c "echo 'kernel.nmi_watchdog=0' >> /etc/sysctl.conf"
NMI watchdog will be disabled every time after next system reboot.
You can also run sudo sysctl -p to disable it without rebooting.
4. Permanently disable NMI watchdog through boot parameter
There's another way to permanently disable it, we've to pass the nmi_watchdog=0 boot time kernel parameter to kernel.
Almost every Linux system uses GRUB as bootloader, so this time it's only for GRUB.
It's easier to manage the boot flags through the /etc/default/grub file in Debian or any Debian based distro like Ubuntu, Linux mint.
First edit the /etc/default/grub file as root and then add nmi_watchdog=0 to the line starting with GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT , after the quiet word.
It should look like below,
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet nmi_watchdog=0 other_parameters"
I used other_parameters just as example, don't use it in your configuration, a screenshot below.
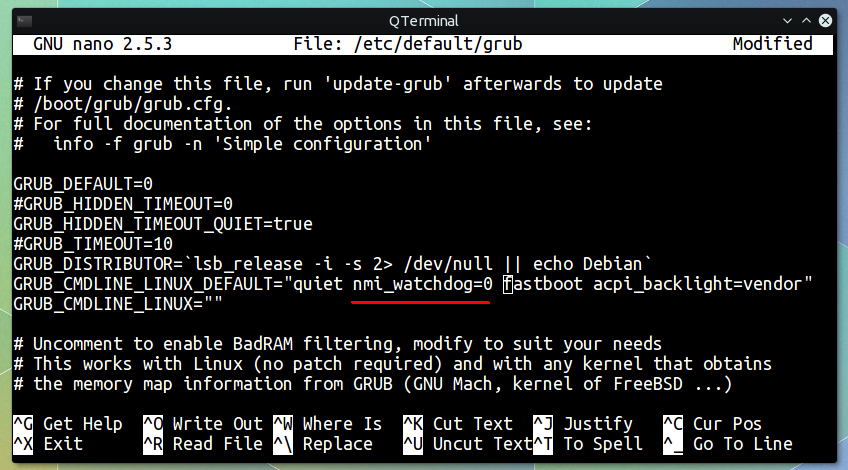
After adding the kernel parameter, don't forget to update the GRUB.
sudo update-grub
Also read- How to disable IPv6 on Linux.
Conclusion
Disabling the watchdog may lock up your system in a very very rare occasion. If you're lucky enough to experience such a moment, then just do a hard reboot, though that's not always possible.
So that's all about how to disable NMI watchdog Linux with command line tools, let us know your reasons for disabling it and which method you're using through the comments.
The Watchdog had conflic with my graphic card and freezed the processes was running, nothing really bad, but had the "WATCHDOG: GPU 1 hangs in OpenCL call, exit NVML: cannot get current temperature, error 15" message, disabled the Watchdog and now my process runs fine. I stoped it making a .sh file with the text:
#!/bin/sh
export GPU_MAX_ALLOC_PERCENT=100
-epsw x -mode 1 -tt 68 -wd 0
Thanks for the tip !
I have the latest CoreFreq installed and have followed exactly what you've said should be done (as regards disabling watchdog) and still get a core dump when using the k(kernel) function in the program.I've become obsessed with this thing and getting seriously frustrated with the fact that I can't get it to stop doing this! Thanks for a neat article.
corefreq-cli': double free or corruption (out): 0x0000563c4da795a0 ***
zsh: abort sudo corefreq-cli
Which distro you're using?
And you don't need to use sudo with
corefreq-cli.